Description
Ana-Zyme P is a biocatalyst specifically formulated to quickly and thoroughly degrade complex proteins commonly found in the anaerobic waste of meatpacking, rendering, food processing, or farming facilities.
Proteinaceous materials are among the most difficult substrates for anaerobic digesters to break down, due to their high nitrogen concentration. They often hinder anaerobic digester performance by passing through the process before they can be completely degraded. Ana-Zyme P bridges the gap between the considerable potential of anaerobic digesters and difficult proteins by breaking them down in a way that methanogens cannot. The rapid hydrolysis of these complex proteins into soluble amino acids creates food and an environment more favorable for methanogenic bacteria.
Aquafix laboratories partners with those who run or operate anaerobic digesters of any kind through technical consulting and biological methane potential testing. Feel free to reach out to us for technical assistance at any time.
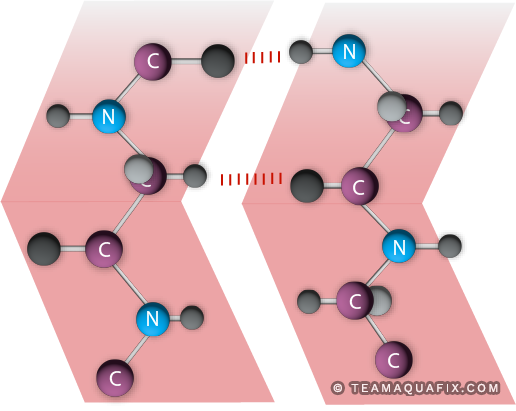
This diagram represents a small part of a protein molecule. Nitrogen (blue atoms) makes up about 16% of the mass of a protein. Generally, anaerobic feed shouldn’t be over 4% nitrogen. In addition, carbon (purple atoms) in proteins is difficult to access anaerobically, making it a poor carbon substrate.
Anaerobic bacteria tend to be poorly specialized for the degradation of protein. Carbohydrates usually make better feed substrates than protein due to their high cBOD content and the low nitrogen requirements of anaerobic bacteria. Fat, oil, and grease—while usually undesirable in a digester—also have a high cBOD content. This means that anaerobic hydrolysis favors the degradation of fats and complex sugars over the degradation of proteins. However, when broken down, protein provides valuable amino acids which improve production of naturally occurring anaerobic enzymes. When free amino acids are absent, anaerobic bacteria need to produce them using simple carbon substrates and ammonia, a process that takes additional metabolic steps and wastes carbon, making the process inefficient.
Ana-Zyme P improves anaerobic efficiency by outsourcing that extra metabolic step in the degradation of proteins so the anaerobic bacteria can focus their resources on breaking down carbon substrates and producing methane. This leads to improved methane generation, lowers effluent COD, and improved volatile solids destruction.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.